Privacy Risks
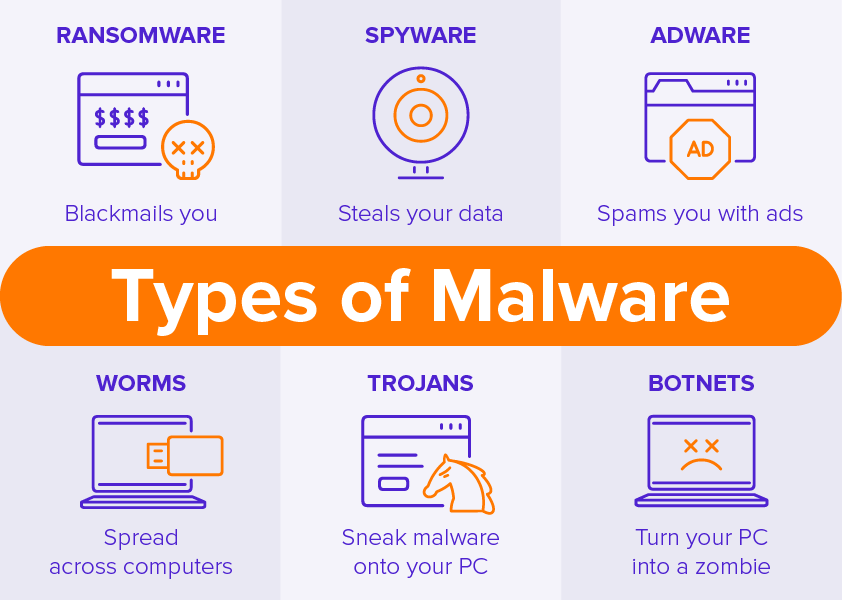
As businesses increasingly rely on cloud databases to store and manage sensitive information, data security has become a critical concern. While these systems offer efficiency and scalability, they also present vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit through data breaches, malware, and unauthorized access. To mitigate these risks, companies implement security measures such as two-factor authentication, firewalls, and antimalware software, serving as the first line of defense against threats.
Beyond basic protections, organizations adopt advanced security strategies like Zero Trust architecture and Trusted Platform Module capabilities to enforce continuous verification of users and devices. Data Loss Prevention tools scan networks for sensitive data, encrypting or deleting unauthorized files, while strict policies regulate data transfers. Insider threats remain a challenge, as employees with privileged access can compromise security, as seen in a 2022 Cash App data breach involving a former employee who stole user information after termination.

Misuse and Protection
Computing resources are often misused in ways that compromise security, including unauthorized file copying, unapproved software installations, and rogue remote access programs. These activities can introduce malware, leading to data breaches and system disruptions. Even seemingly harmless actions, like excessive personal web browsing or media streaming, can degrade network performance and increase security risks.
One major incident occurred in 2021 when an Okta employee installed unauthorized software, inadvertently introducing malware that led to a data breach, exposing sensitive customer information. To prevent such threats, organizations enforce strong password policies, regularly update software, use firewalls, and monitor network activity for suspicious behavior. Establishing clear security protocols helps users understand the risks and adhere to proper usage guidelines.


Unauthorized Access
Hackers use various techniques to exploit security vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to sensitive information. Phishing is a common method where attackers impersonate trusted sources to steal login credentials or personal data through deceptive emails containing malicious links or attachments. Other tactics include cracking weak passwords, executing brute force attacks, and exploiting unpatched software to infiltrate databases, often resulting in financial and reputational damage.
To combat these threats, organizations implement firewalls, antivirus software, and two-factor authentication to enhance security. Advanced measures like endpoint security and network monitoring detect suspicious activity, while encryption ensures stolen data remains unreadable. Regular cybersecurity training also helps employees recognize phishing scams. A notable example occurred in 2016 when hackers used phishing emails to breach the Democratic National Committee, resulting in the exposing of confidential data.


Benefits and Risks
Computing innovations have improved efficiency and accessibility across fields like healthcare, education, and communication. AI-powered diagnostics help doctors detect diseases earlier, while platforms such as Zoom and Google Classroom make learning more accessible worldwide. Despite these benefits, risks such as data privacy concerns and cybersecurity threats have increased as more personal information is stored online, leaving users vulnerable to hacking and identity theft.
Social media exemplifies both the positive and negative impacts of technology. While platforms like Facebook and Twitter enhance global communication, they also contribute to misinformation, cyberbullying, and privacy violations. The 2018 Cambridge Analytica scandal highlighted the dangers of data misuse, sparking concerns about political manipulation. Similarly, facial recognition technology improves security but raises ethical questions about surveillance and discrimination, emphasizing the need for careful regulation.









